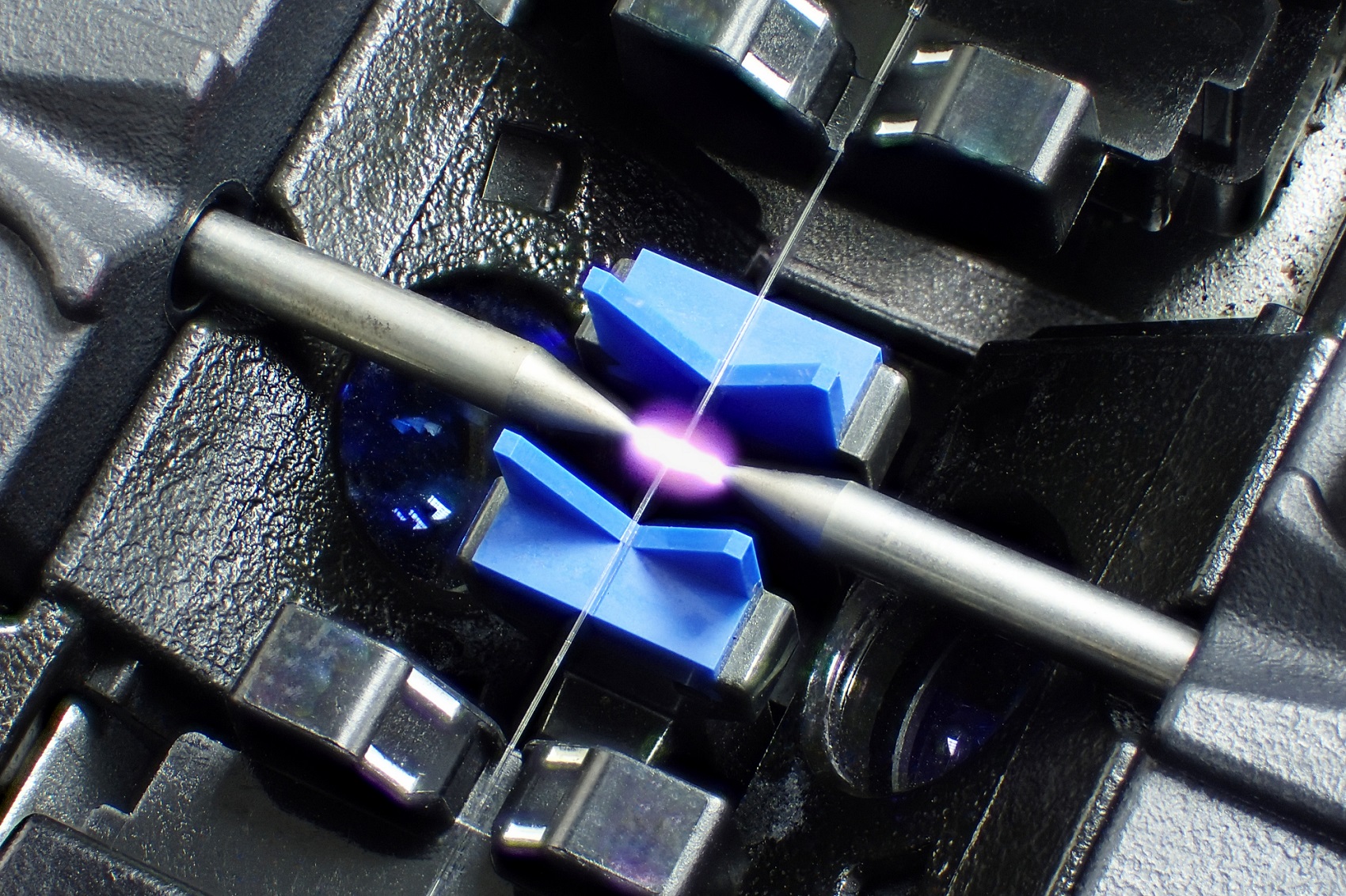
What is fibre splicing?
Fibre splicing is the process involving the fusion of the fibre within two fibre optic cables to provide a continuous optical path for transmitting light signals. By effectively splicing fibre cables, technicians can ensure a reliable and efficient network infrastructure. As well as being a fundamental technique used in the installation and maintenance of fibre optic networks, splicing is used to repair these cables. Fibre optic cables can be buried, installed in a duct, or overhead, and can all be repaired if damaged.
What are the benefits of fibre splicing?
- Network reliability: Ensures the integrity of the network by eliminating potential weak points, such as connectors or mechanical joints. Connectors join optical fibres together but often take up a lot of space in the panel and have a higher back reflection. Fibre splicing significantly reduces signal loss, minimizes network downtime, and enhances overall reliability.
- Increased bandwidth: Another benefit is that it enables the creation of longer cable runs without compromising signal quality. By splicing multiple fibres together, network operators can extend their reach, enabling higher bandwidth and accommodating future growth.
- Cost efficiency: It also offers cost advantages by reducing the need for additional hardware, such as connectors and couplers. Moreover, splicing eliminates the requirement for signal conversion between different types of connectors, resulting in a more streamlined and cost-effective network.
- Space saving: You can fit more splices in a smaller space compared to connectors. Using splice trays, you can organise the splices for compact storage.
Is there more than one method of fibre splicing?
There are two methods of splicing: fusion and mechanical.
Fusion splicing is the most common method used in fibre optic networks. It involves permanently joining two fibre ends by melting them together using an electric arc or laser. This process ensures low signal loss and high mechanical strength. Fusion splicing is typically performed using specialised fusion splicing machines which heat the fibre ends with electrodes and fused.
Mechanical splicing involves aligning and joining fibre ends using mechanical components such as connectors or sleeves. Although it does not provide the same level of performance as fusion splicing, it offers a cost-effective solution for temporary connections or emergency repairs. It does not require a fusion splicer.
Fibre splicing is an essential process that ensures the reliable and efficient transmission of data in fibre optic networks. By eliminating weak points and enhancing signal integrity, splicing plays a vital role in maintaining a robust network infrastructure. As technology continues to evolve, splicing will remain a critical skill, empowering us to stay connected in the digital age.
Enabling seamless fibre connections
As the world becomes increasingly digitalised, seamless connectivity is becoming indispensable. Fibre optic networks are seen as the backbone of our digital world, thanks to their high bandwidth and reliability. The process of fibre splicing plays a crucial role in ensuring uninterrupted data transmission.
To build these fibre networks, it is essential that the right components and accessories are installed to enable fast, reliable connections. The Prysmian Connectivity Selector Tool calculates and recommends the correct fibre closure based on the requirements of each individual installation, quickly and efficiently.
Discover more about how Prysmian are advancing connectivity.